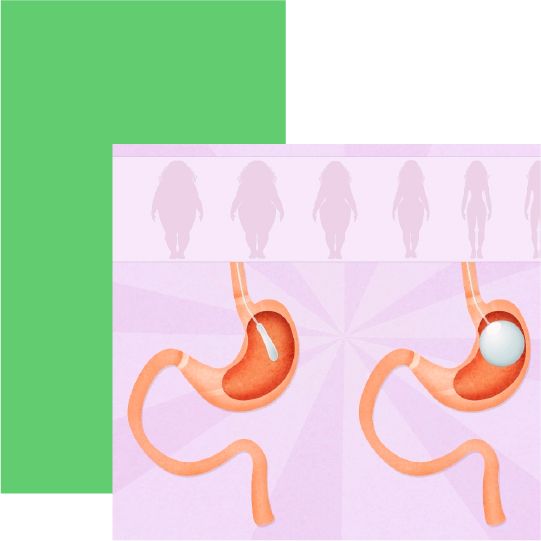
Gastric balloon – less space for food
A gastric balloon can be made of silicone or plastic. In most cases, the gastric balloon is inserted into the stomach by gastroscopy in Turkey, where its volume creates an earlier feeling of satiety. This is intended to encourage patients to eat less. In combination with a conscious diet, the balloon can bring about weight loss and is considered a supportive measure for dietary change, because without a consistent change in lifestyle and eating habits, the intragastric balloon hardly leads to weight reduction. This therapy is also not suitable for rapid weight loss, since after removal of the balloon a yo-yo effect is promoted, which quickly motivates the patient to gain weight again. The gastric balloon has proven particularly useful as part of a “multi-step therapy” for weight loss in high-risk patients before obesity surgery such as gastric bypass or gastric reduction becomes necessary.
Gastric balloon for severely overweight patients
The gastric balloon is considered for severely overweight patients who have not been able to reduce their weight in the past through dietary changes or exercise. From which initial weight a gastric balloon is considered, varies greatly and depends on the sex and height of the patient. The body mass index (BMI) serves as a guideline. Depending on the patient, the balloon can be inserted at a BMI of 28 or higher. This BMI – also body mass index, body mass number or Quetelet-Kaup index – is a measure for evaluating a person’s body weight in relation to their height. The BMI is calculated by dividing the body weight in kilograms by the height in meters squared. As BMI, or obesity, increases, the risk of obesity-related diseases increases. The gastric balloon does not work for severe inflammation of the digestive tract, blood clotting disorders, psychiatric disorders and drug problems, as well as for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Applying a Gastric Balloon
Unlike gastric banding and gastric reduction, the gastric balloon is a non-surgical treatment to reduce severe obesity. One type is a so-called swallow balloon. The patient swallows a capsule about three centimeters long, into which the doctor then fills about 250 milliliters of non-toxic inert gas through a tube. The tube is then removed.
In variant two, the intragastric balloon is inserted during a gastroscopy. The physician uses a gastroscope to place the balloon in the stomach through the esophagus. Using the video optics of The gastroscope, the doctor can see whether the stomach lining is healthy and therefore suitable for a gastric balloon. The balloon is then filled with 500 to 700 milliliters of saline solution through the gastroscope. The saline is generally mixed with a special blue dye to check via urine whether the balloon is tight.
The procedure itself is performed on an outpatient basis and after sedation. It generally takes between twenty and thirty minutes. Afterwards, the patient remains in the clinic for one to two hours for monitoring. Some patients suffer from nausea and vomiting after balloon insertion. They receive saline intravenously. Therefore, a short hospital stay may be required for these patients.
Weight loss results through the balloon
The filled balloon occupies a large part of the stomach. The patient feels full faster because the capacity of the stomach is reduced. A gastric balloon can remain in the body for up to twelve months. After that, the gastric balloon is removed by gastroscope in Turkey to prevent damage to the stomach lining. How long the balloon remains in the stomach also determines the weight loss success. An average of 15 – 20 kg is the rule. A 12-month treatment increases the weight loss success compared to a 6-month treatment. With a one-year balloon, about 30 kg – with very motivated patients even up to 50 kg – weight loss is possible. The patient must be aware that a gastric balloon is only useful if one wants to change one’s lifestyle habits. That means eating healthier and exercising more. After all, once the balloon is removed again, one can theoretically eat just as much as before and quickly gain weight again. For this reason, patients should opt for multimodal gastric balloon therapy, which includes parallel systematic nutritional counseling, appropriate exercise training, and behavioral and motivational coaching. These measures increase the likelihood of achieving the desired weight loss success.

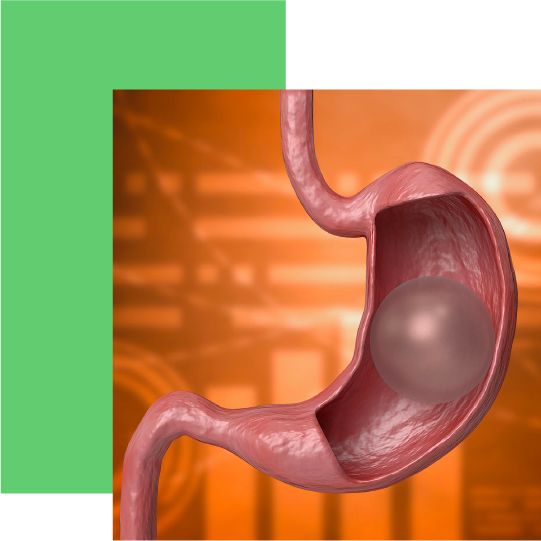
Possible Side Effects
Nausea may occur during the first few days after the gastric balloon is placed. Stomach pain may also occur, but after a few days, patients will have become accustomed to the foreign part in the stomach. Patients with a gastric balloon need to be aware that they are at increased risk for stomach ulcers. Improper diet can also lead to a fluid deficit with disturbances in salt balance. If a fluid-filled gastric balloon bursts, which the affected person notices immediately by the blue coloration of his urine, it must be removed immediately by endoscopy. This prevents the balloon remnant from escaping before it can provoke an intestinal obstruction. Difficulties may also arise in sedating overweight patients. In addition to the usual risks of anesthesia, in rare cases gastric juice is inhaled into the trachea and lungs, which can lead to pneumonia.
Advantages and disadvantages of a gastric balloon
Advantages
– Weight loss without surgery.
– No or only temporary side effects.
– With a healthy lifestyle, the new weight can be maintained.
– No surgery -only a short recovery time is needed.
Disadvantages
– Taking stomach acid inhibitors while the gastric balloon is in the stomach.
– The gastric balloon is generally not covered by health insurance.
– After the intragastric balloon is placed, there may be brief discomfort.






